China has sent warships, including an aircraft carrier, into the seas around Taiwan.
Beijing’s latest show of military force followed a meeting on Wednesday in California between Taiwan’s President Tsai Ing-wen and US House Speaker Kevin McCarthy.
China sees self-ruled Taiwan as a breakaway province that will eventually be under Beijing’s control.
China’s President Xi Jinping has said “reunification” with Taiwan “must be fulfilled” – and has not ruled out the possible use of force to achieve this.
But Taiwan sees itself as distinct from the Chinese mainland, with its own constitution and democratically-elected leaders.
Where is Taiwan?
Taiwan is an island, roughly 100 miles from the coast of south-east China.
It sits in the so-called “first island chain”, which includes a list of US-friendly territories that are crucial to US foreign policy.
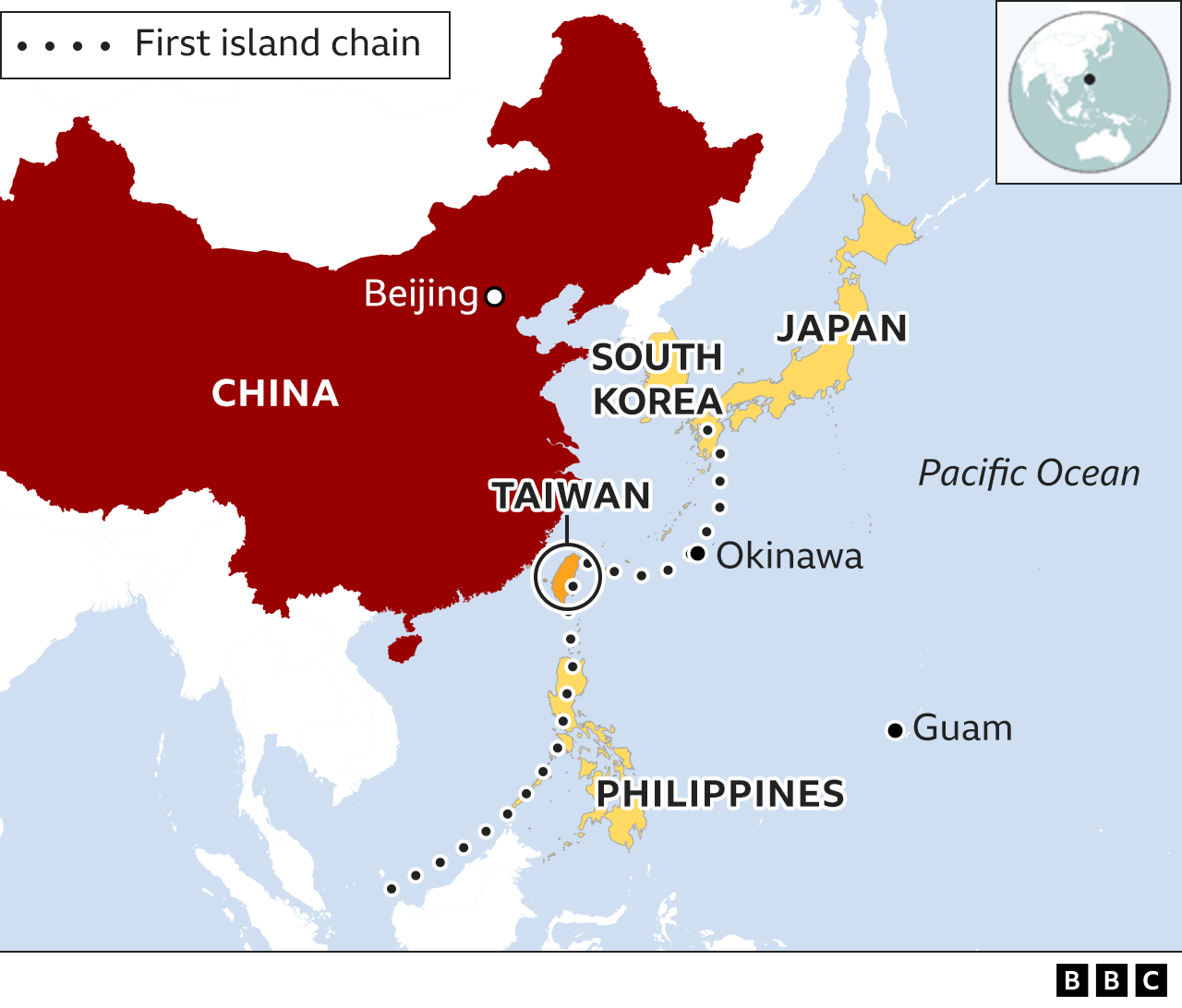
If China was to take over Taiwan, some Western experts suggest it could be freer to project power in the western Pacific region and could possibly even threaten US military bases as far away as Guam and Hawaii.
But China insists that its intentions are purely peaceful.
Has Taiwan always been separate from China?
Historical sources suggest that the island first came under full Chinese control in the 17th Century when the Qing dynasty began administering it. Then, in 1895, they gave up the island to Japan after losing the first Sino Japanese war.
China took the island again in 1945 after Japan lost World War Two.
But a civil war erupted in mainland China between nationalist government forces led by Chiang Kai-shek and Mao Zedong’s Communist Party.
The communists won in 1949 and took control in Beijing.
Chiang Kai-shek and what was left of the nationalist party – known as the Kuomintang – fled to Taiwan, where they ruled for the next several decades.
China points to this history to say that Taiwan was originally a Chinese province. But the Taiwanese point to the same history to argue that they were never part of the modern Chinese state that was first formed after the revolution in 1911 – or the People’s Republic of China that was established under Mao in 1949.

The Kuomintang has been one of Taiwan’s most prominent political parties ever since – ruling the island for a significant part of its history.
Currently, only 13 countries (plus the Vatican) recognise Taiwan as a sovereign country.
China exerts considerable diplomatic pressure on other countries not to recognise Taiwan, or to do anything which implies recognition.
Can Taiwan defend itself?
China could attempt to bring about “reunification” by non-military means such as strengthening economic ties.
But in any military confrontation, China’s armed forces would dwarf those of Taiwan.
China spends more than any country except the US on defence and could draw on a huge range of capabilities, from naval power to missile technology, aircraft and cyber attacks.
Much of China’s military power is focused elsewhere but, in overall terms of active duty personnel for example, there is a huge imbalance between the two sides.
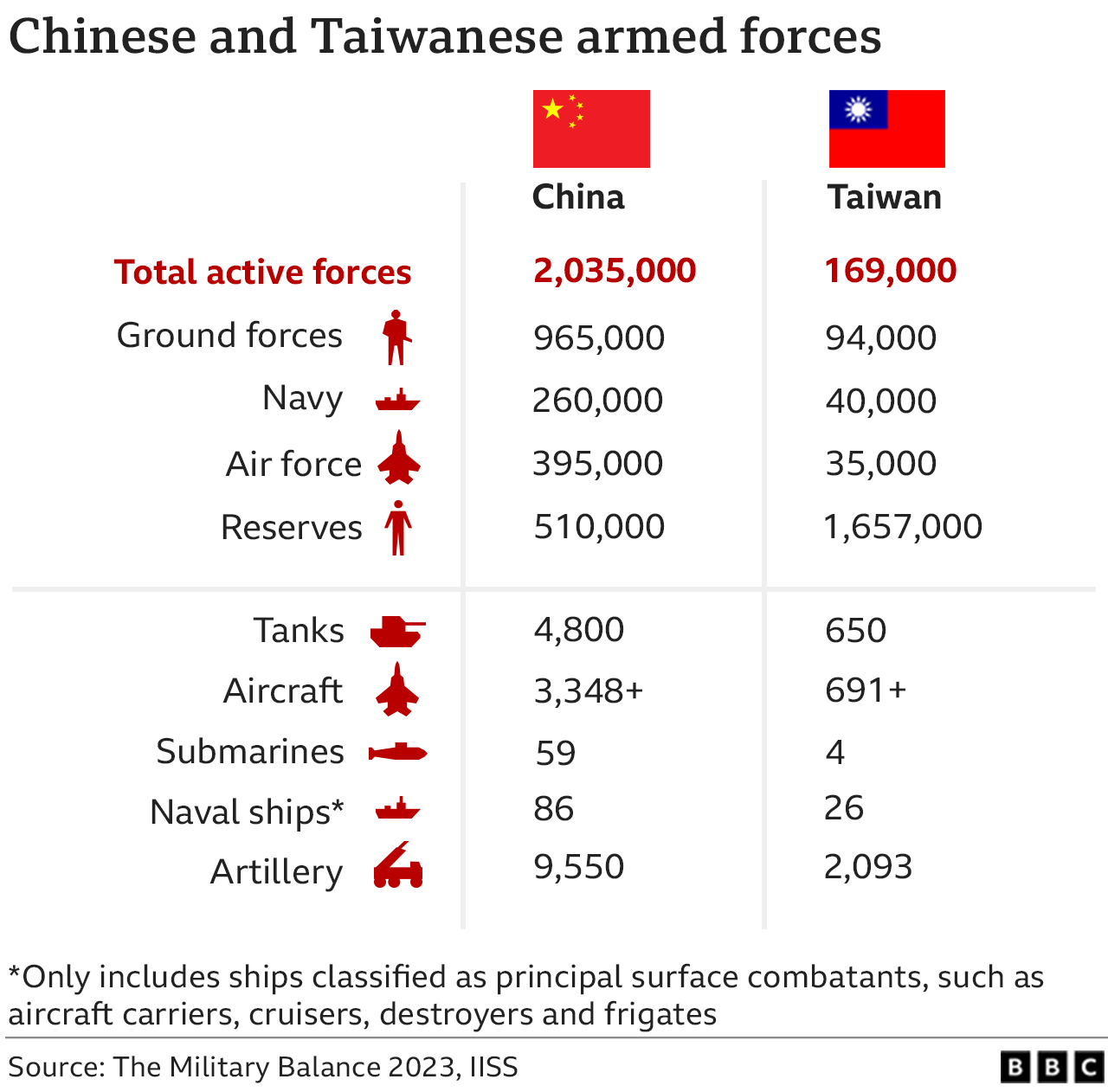
In an open conflict, some Western experts predict that Taiwan could at best aim to slow a Chinese attack, try to prevent a shore landing by Chinese amphibious forces, and mount guerrilla strikes while waiting for outside help.
That help could come from the US which sells arms to Taiwan.
Until now, Washington’s policy of “strategic ambiguity” has meant the US has been deliberately unclear about whether or how it would defend Taiwan in the event of an attack.
Diplomatically, the US currently sticks to the “One-China” policy, which recognises only one Chinese government – in Beijing – and has formal ties with China rather than Taiwan.
But in May last year, US President Joe Biden appeared to harden Washington’s position.
Asked whether the US would defend Taiwan militarily, Mr Biden replied: “Yes.”
The White House insisted that Washington had not changed its position.
Is the situation getting worse?
Relations between Taiwan and China deteriorated sharply following a visit to the island by the then US House Speaker, Nancy Pelosi, in August 2022.
Beijing condemned Ms Pelosi’s visit as “extremely dangerous”.
China launched a series of military exercises, including the firing of ballistic missiles, focused on six danger zones around Taiwan, three of which overlapped the island’s territorial waters.
Taiwan said the move, which forced ships and planes to find routes around those areas, violated its sovereignty and amounted to a blockade.
Tensions between China and Taiwan had already been increasing.
In 2021, China appeared to ramp up pressure by sending military aircraft into Taiwan’s Air Defence Zone, a self-declared area where foreign aircraft are identified, monitored, and controlled in the interests of national security.
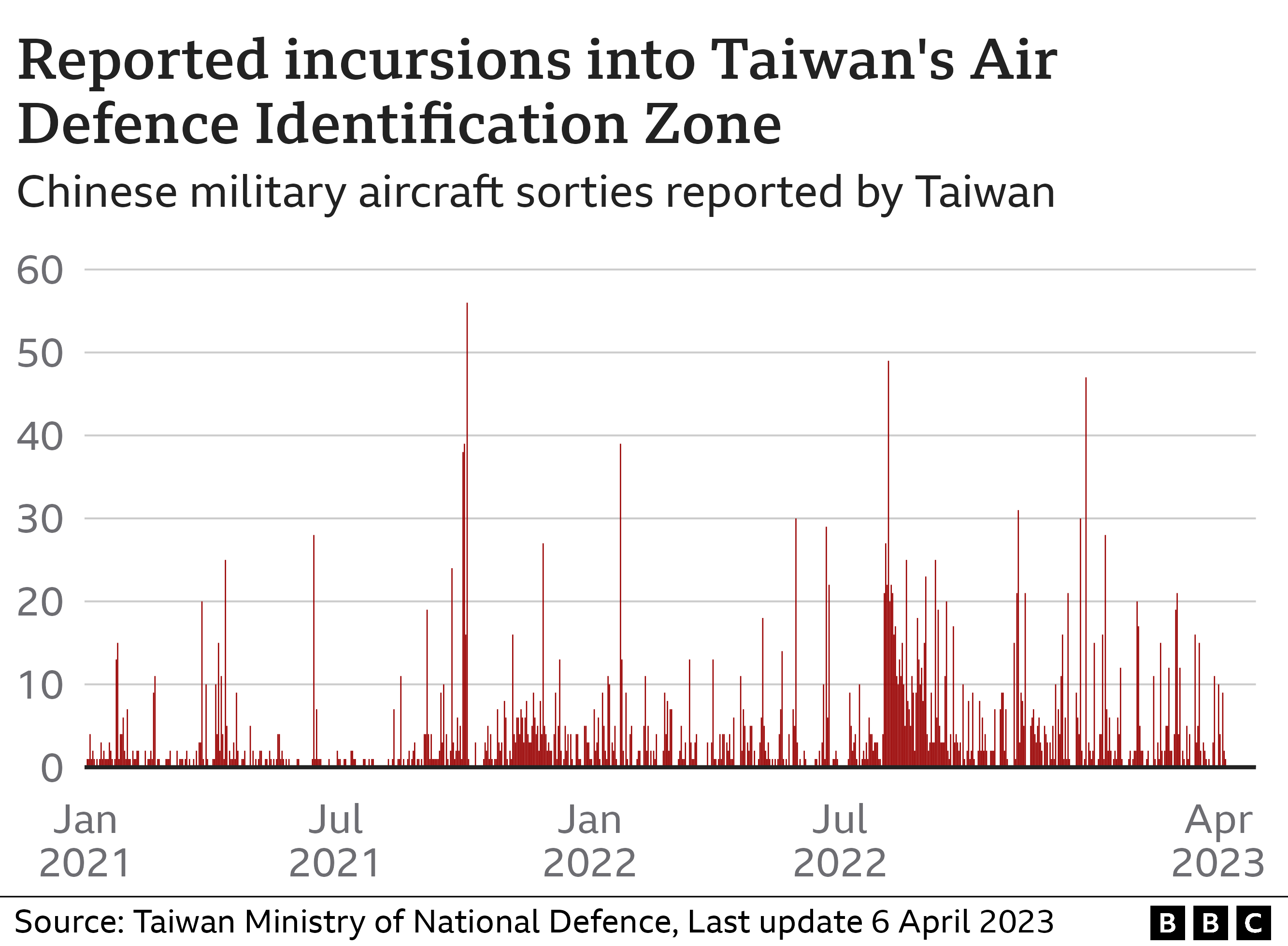
The numbers of aircraft reported peaked in October 2021 at 56 incursions in a single day, with Taiwan’s defence minister saying relations were the worst they had been for 40 years.
Since then there have been 22 days with more than 20 incursions reported.
Taiwan made data on plane incursions public in 2020.
China’s coastguard claims it has the legal authority to stop and inspect shipping in the area around Taiwan.
On Wednesday, it said “on-site inspections” on some vessels would commence.
Taiwan has objected to the move and has instructed Taiwanese vessels not to co-operate with attempts to board and inspect them.
Why is Taiwan important for the rest of the world?
Taiwan’s economy is hugely important.
Much of the world’s everyday electronic equipment – from phones to laptops, watches and games consoles – is powered by computer chips made in Taiwan.
By one measure, a single Taiwanese company – the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company or TSMC – has over half of the world’s market.
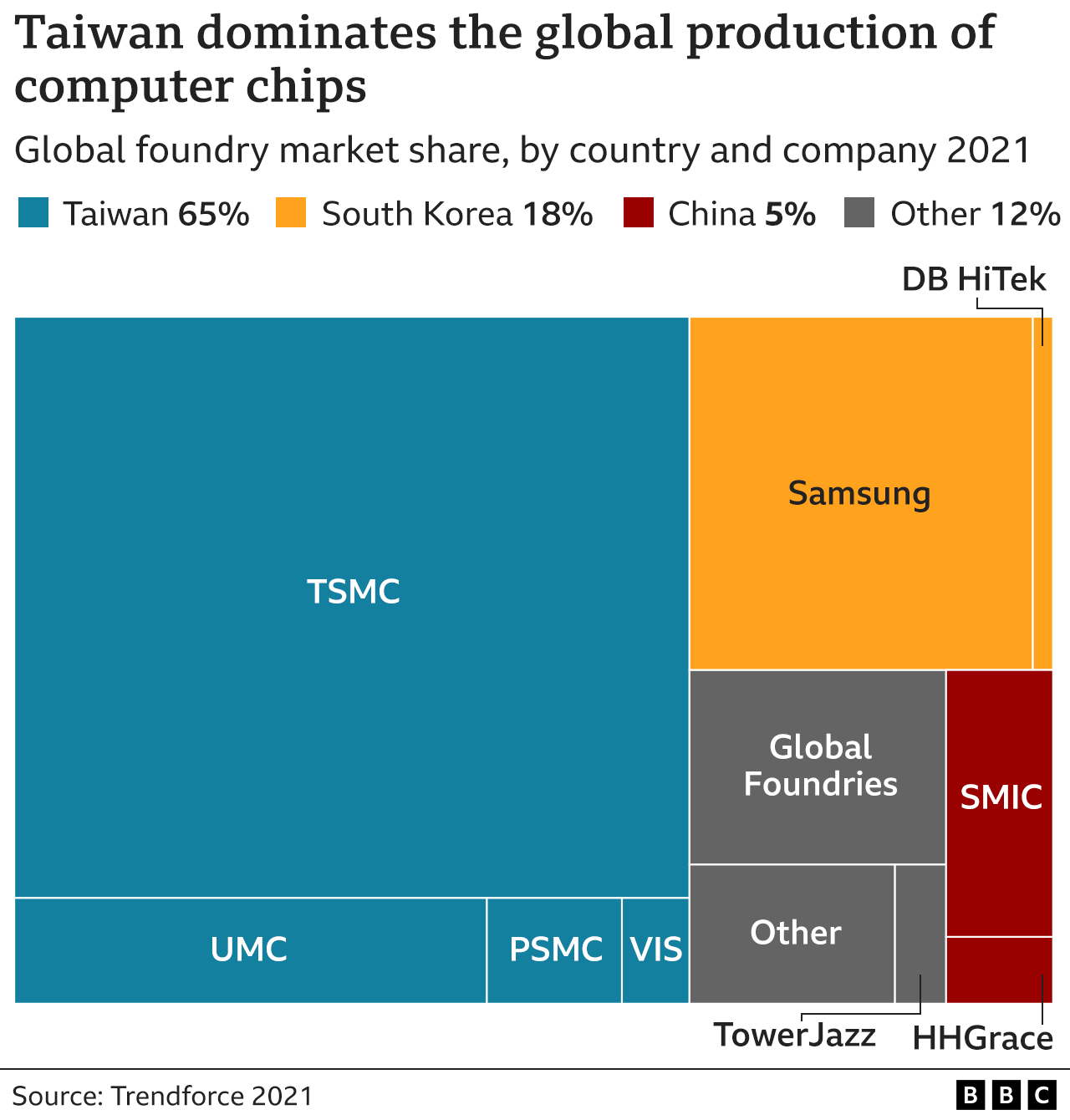
TSMC is a so-called “foundry” – a company which makes chips designed by consumer and military customers. It is a vast industry, worth almost $100bn (£73bn) in 2021.
A Chinese takeover in Taiwan could give Beijing some control over one of the world’s most important industries.
Are the Taiwanese people worried?
Despite the recent tensions between China and Taiwan, research suggests that many Taiwanese people are relatively untroubled.
In October 2021 the Taiwan Public Opinion Foundation asked people whether they thought that there would, eventually, be war with China.
Almost two thirds (64.3%) replied that they did not.
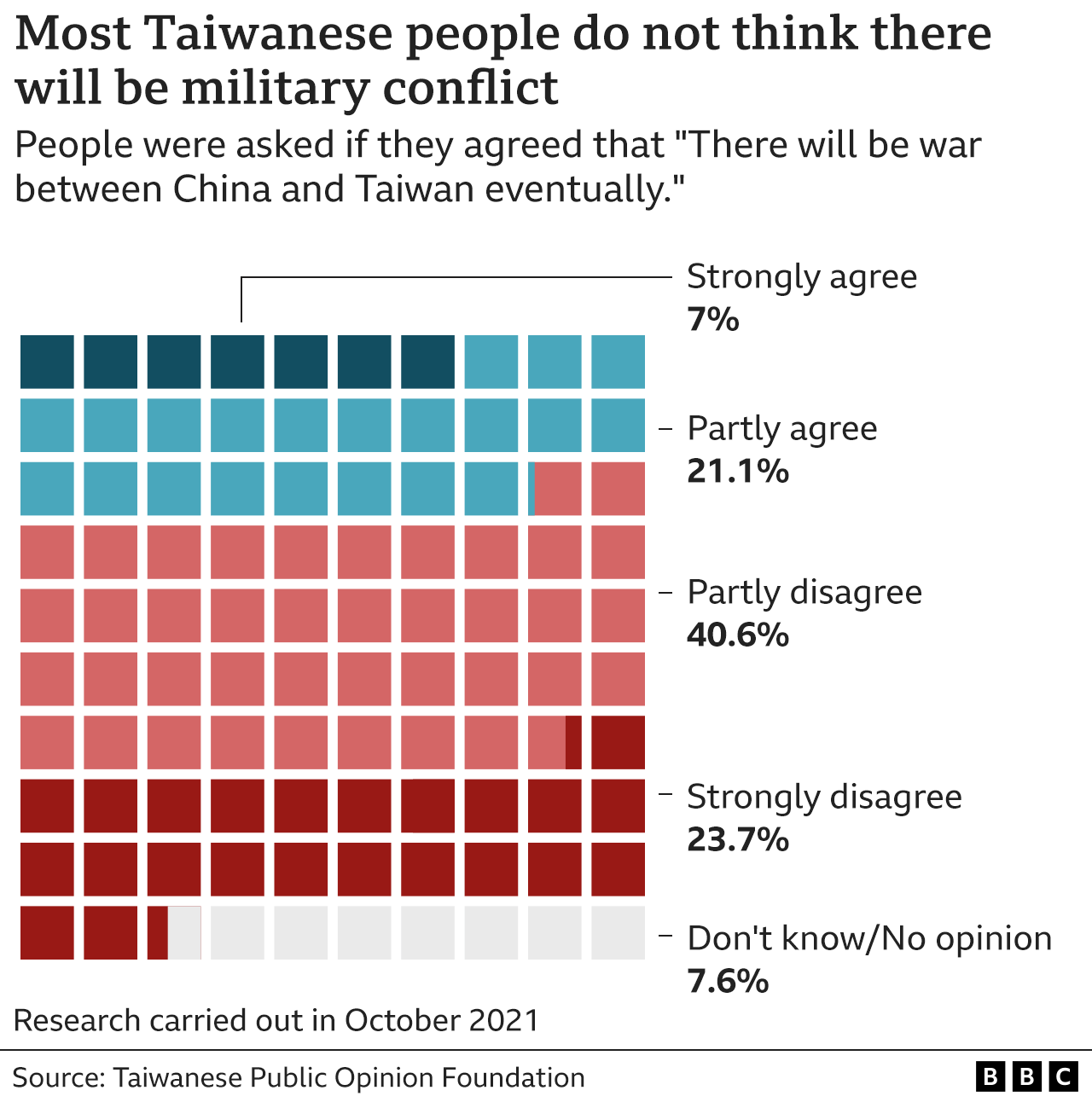
Separate research indicates that most people in Taiwan identify as Taiwanese – embracing a distinctly different identity.
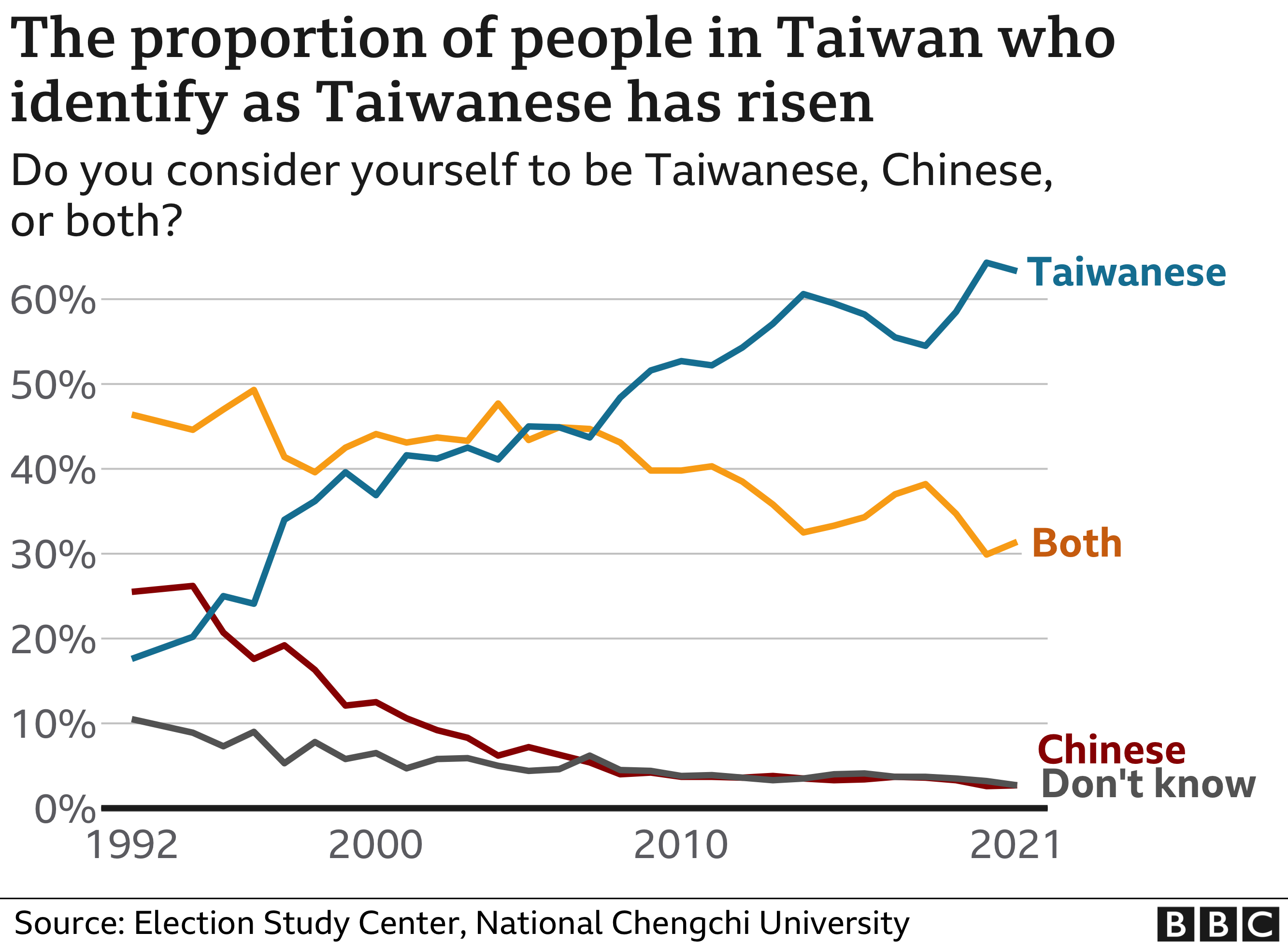
Surveys conducted by the National Chengchi University since the early 1990s indicate that the proportion of people who identify as Chinese, or both Chinese and Taiwanese, has fallen and that most people consider themselves as Taiwanese.
Source: BBC
















